Genomics, and the promise of precision medicine
-
- from Shaastra :: vol 03 issue 05 :: Jun 2024

The potent new tool is helping to unlock new realms of personalised healthcare.
howindialives.com
howindialives.com is a database and search engine for public data
Precision medicine, or personalised medicine, is changing the way the healthcare system understands, diagnoses and treats diseases. It takes into account individual differences in people's genes, environments, and lifestyles, marking a significant shift from the ‘one-size-fits-all' approach to treating diseases and illnesses. One of the most potent tools of this approach is genomics, the study of the genome, or the complete set of genes, of an organism.
THE PROMISE OF PRECISION MEDICINE
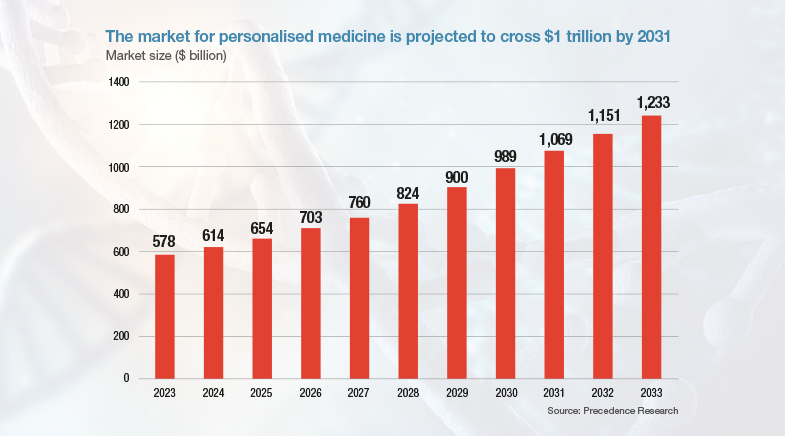
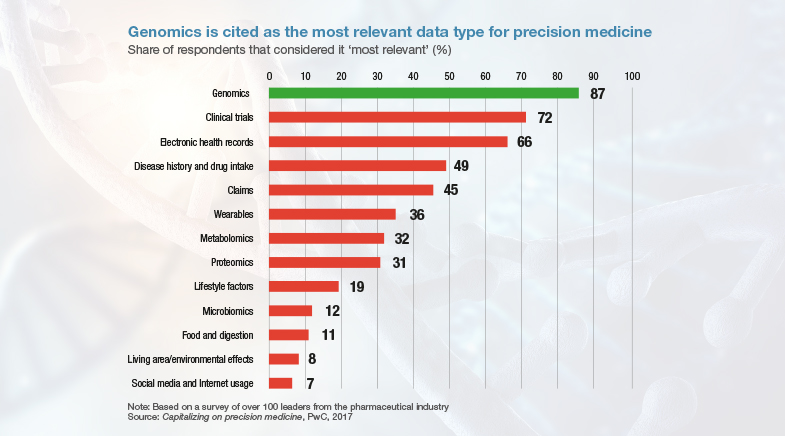
According to Precedence Research, the size of the personalised medicine market is set to grow from $578 billion in 2023 to $1.23 trillion by 2033. It enhances the ability of doctors and researchers to predict more effective treatments for a specific group of people, by helping them better understand the genetic make-up of a person or the genomic characteristics of a disease. It is already being applied in oncology and holds promise for a range of health problems, including cardiovascular conditions and infectious diseases. According to a 2017 survey of pharmaceutical leaders by consulting firm PwC, genomics provides the most relevant data types for precision medicine.
THE GENOMICS REVOLUTION
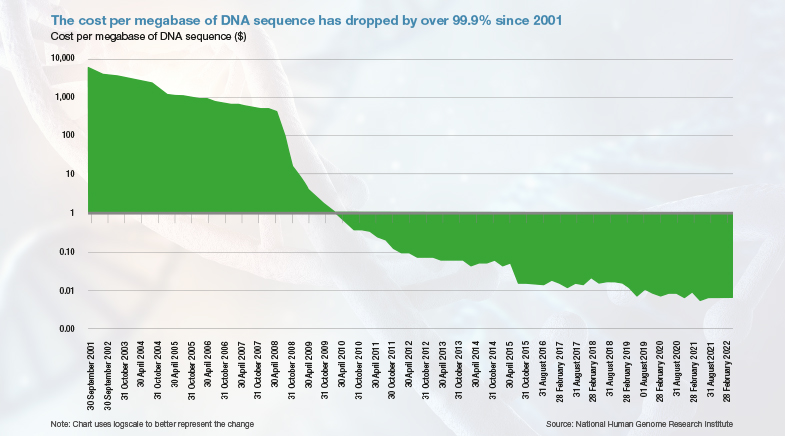
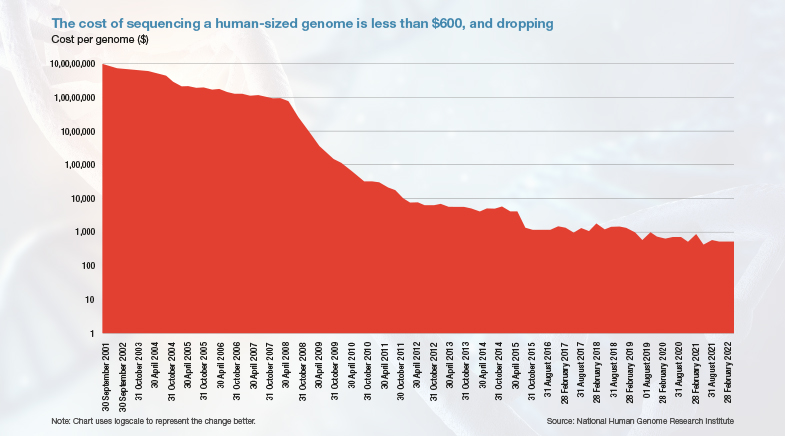
The first Human Genome Project is estimated to have cost $2.7 billion. The cost has been continuously sliding down, thanks to technological innovations. Both the cost of determining smaller chunks (measured in megabase of DNA sequence) and the cost of sequencing entire human genomes have fallen. According to the National Human Genome Research Institute, based in Maryland, U.S., the drop in costs outpaced Moore’s Law (which led to a dramatic fall in computing costs) since 2008, as sequencing transitioned to second-generation technologies.
THE PULL OF THE MARKET
The private sector has built on the successes of the Human Genome Project and other genomic research, leading to a broad array of commercial opportunities. Companies such as Illumina and Thermo Fisher Scientific offer sequencing services as well as instruments, reagents and software. Similarly, 23andMe provides genetic testing for less than $100. There are at least nine companies with a market capitalisation of over $2 billion. The rate at which the U.S. Food & Drug Administration is approving cell and gene therapy products has increased in the last few years, and is expected to go up.
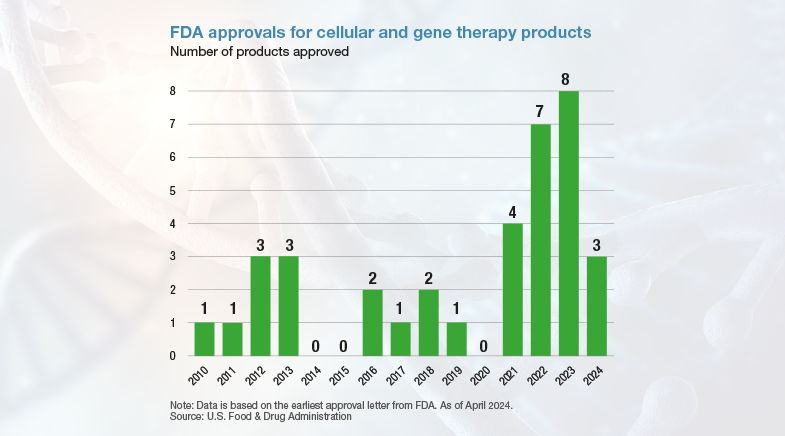
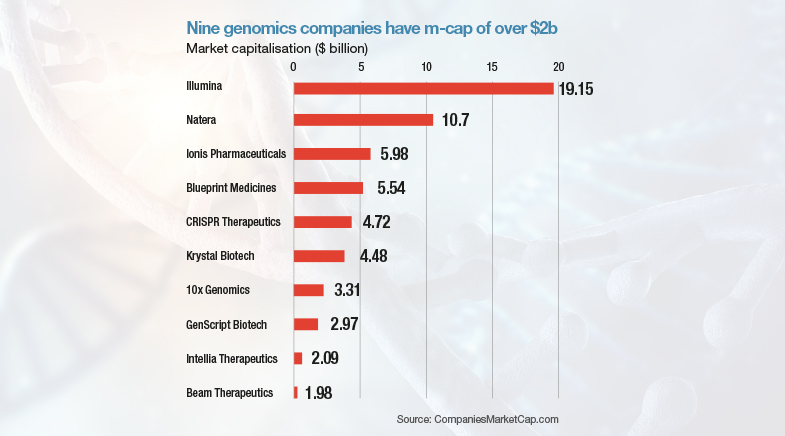
THE INNOVATION PORTFOLIO
Genomics is expected to advance further even as related and more specific technologies progress. For example, CRISPR (Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats) technology, which has attracted huge research interest, allows scientists to add, delete, or alter sections of the DNA sequence. It enables them to study the function of specific genes and develop therapies for genetic diseases. As CRISPR technology continues to evolve, it promises to accelerate genomics research and open up new possibilities in personalised medicine. Similarly, bioinformatics, the application of computational technology to handle the rapidly growing repository of information related to genomics, is set to play a crucial role. Recent advances in artificial intelligence could further provide a boost to genomics research and application.
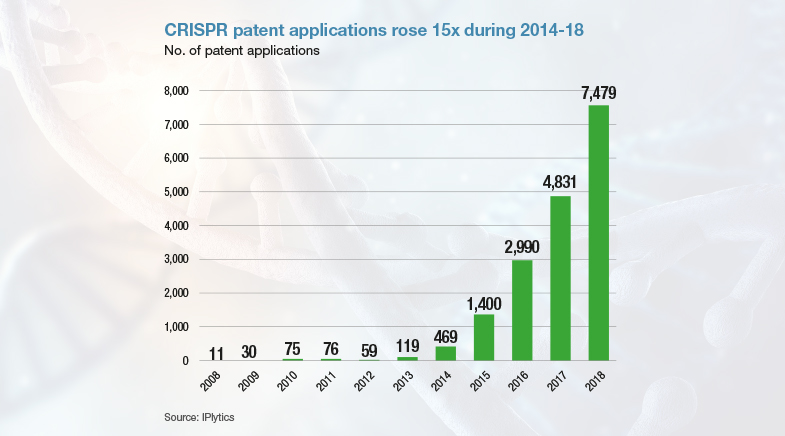
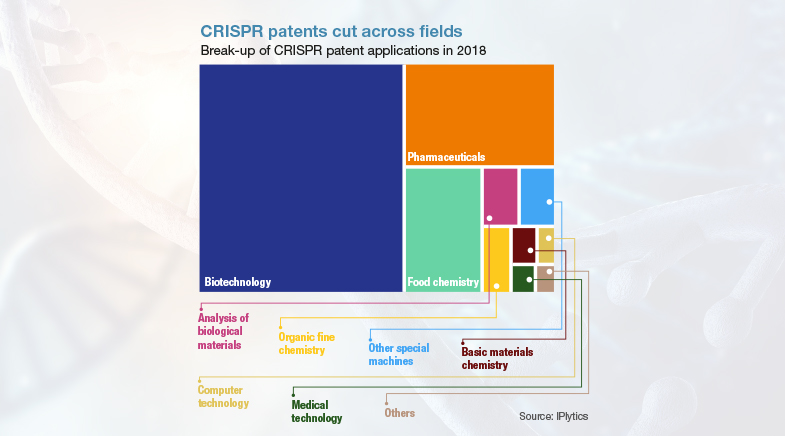
See also:
Have a
story idea?
Tell us.
Do you have a recent research paper or an idea for a science/technology-themed article that you'd like to tell us about?
GET IN TOUCH














