Plugged into the future of brain-computer interface
-
- from Shaastra :: vol 03 issue 08 :: Sep 2024
Investments in brain-computer interface are driving new technologies.
howindialives.com
howindialives.com is a database and search engine for public data
Neuralink, a brain-computer interface (BCI) company founded by maverick entrepreneur Elon Musk and a team of engineers and scientists, has implanted its devices in two patients: the first in January 2024, and the second more recently. (Musk announced it in early August, along with plans for eight more implants in the rest of 2024, subject to regulatory approval.) The implants allow patients to communicate with and control digital devices merely by thinking. Noland Arbaugh, the first patient to get a device, said the BCI technology has reduced his reliance on caregivers, giving him more independence.
THE FUNDING
BCI enables direct communication between the brain and external devices. Scientists have been working on the idea since the 1960s, making steady progress. However, in the shorter run, they are primarily targeting individuals with severe motor disabilities, such as paralysis and degenerative neurological diseases.
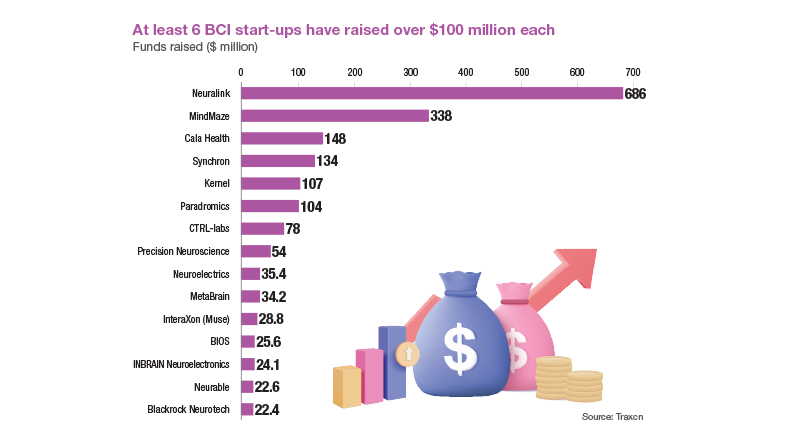
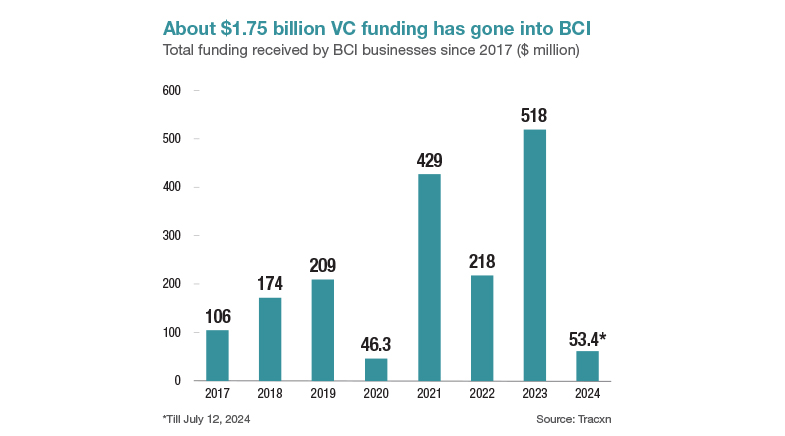
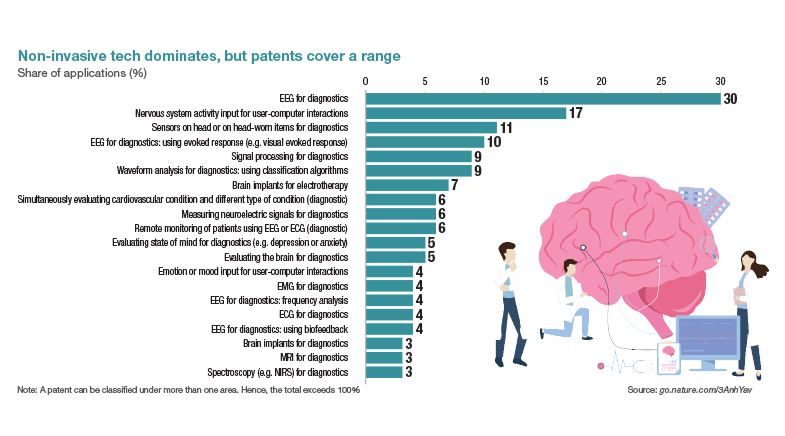
Neuralink is one of the many start-ups taking BCI to market. Besides Neuralink, at least five other BCI start-ups — including MindMaze, Cala Health and Synchron — have received over $100 million in funding since their founding. Venture capital investments into BCI start-ups grew from $106 million in 2017 to $518 million in 2023. While this growth reflects the potential that investors see in the market, it has also been driving cutting-edge technology. This ranges from non-invasive methods like electroencephalography (EEG) and functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI), which capture brain signals from outside the skull, to increasingly invasive approaches involving implanted electrodes.
THE TECHNOLOGY
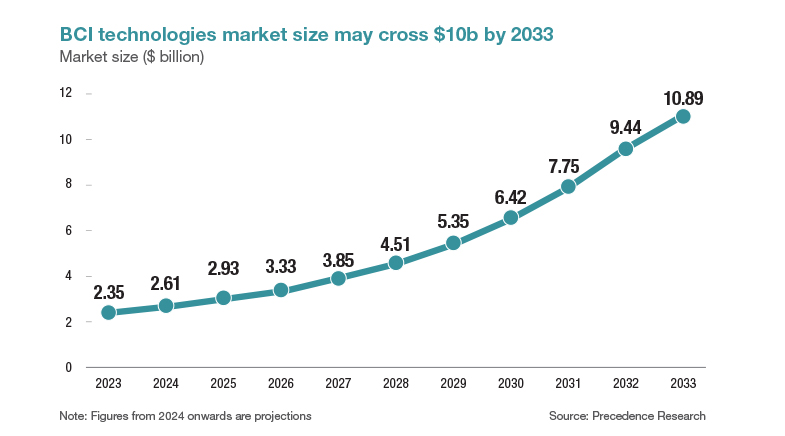
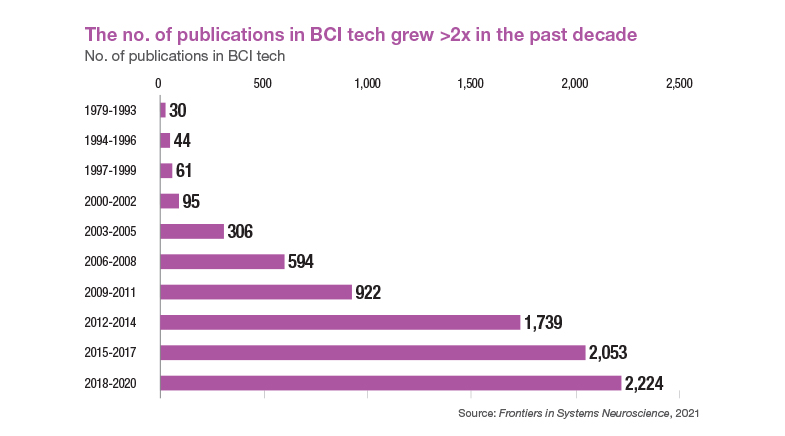
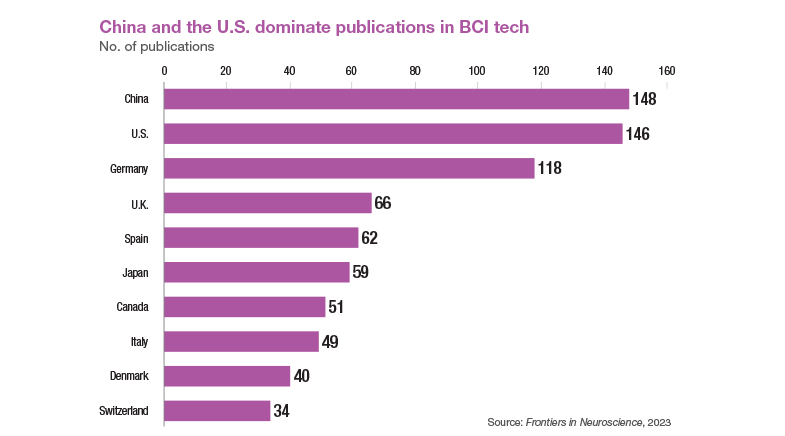
While the BCI market is estimated to cross $10 billion by 2033, the foundation for the development of this technology has been laid by decades of research. In the past decade, the number of papers in this field has doubled. This foundational knowledge has been significantly advanced by breakthroughs in related fields. Miniaturisation has enabled the creation of smaller, more powerful sensors and implants, while advancements in signal processing and computational power have improved the ability to interpret brain signals. Additionally, innovations in materials science have led to the development of biocompatible and durable implants.
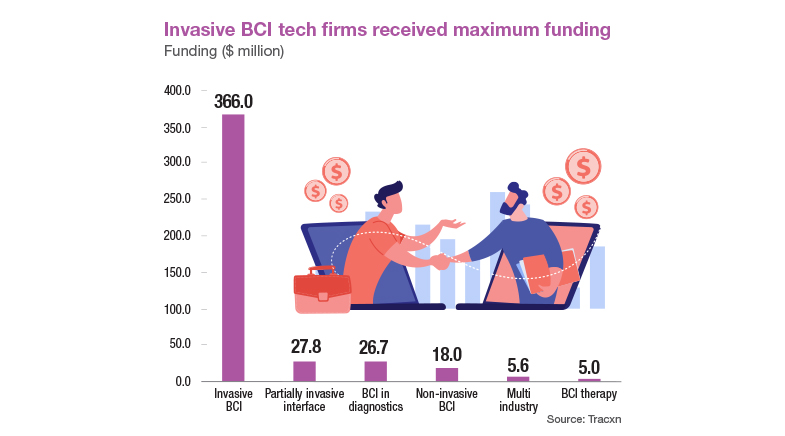
These advancements have pushed the development of both invasive and non-invasive BCIs. While non-invasive methods, such as EEG, offer accessibility and safety, invasive approaches, like those involving implanted electrodes, provide higher-resolution data. These technologies have potential applications across a wide spectrum, from diagnosis to communication and control.
THE HOTSPOTS
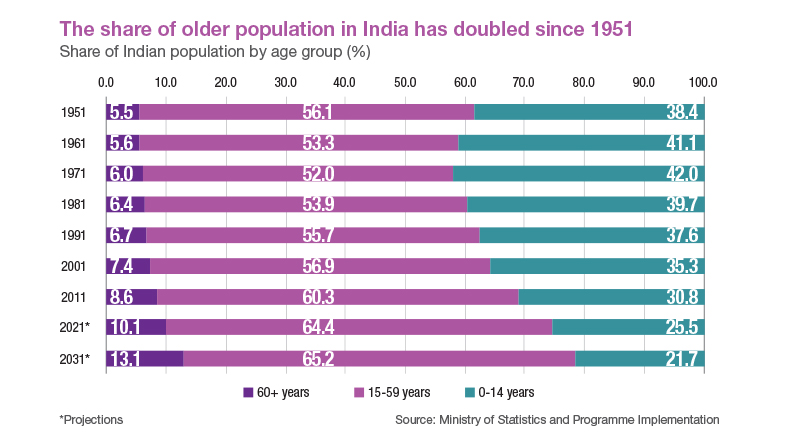
Neurological disorders such as paralysis, Parkinson's disease, and epilepsy affect millions globally; the current treatment options often fall short. BCI technology could alleviate these debilitating conditions. Besides, as the world grapples with an ageing population, these technologies could also address age-related neurological challenges like dementia and Alzheimer's disease. The World Health Organization estimates that a sixth of the global population will be aged over 60 and above by 2030. In India, the share of people above 60 years of age has increased from 5.5% in 1951 to 10.1% in 2021, and is expected to expand further to 13.1%. BMI technology promises to improve the quality of their lives significantly, especially as applications expand, performance gets better and costs come down in the coming years.
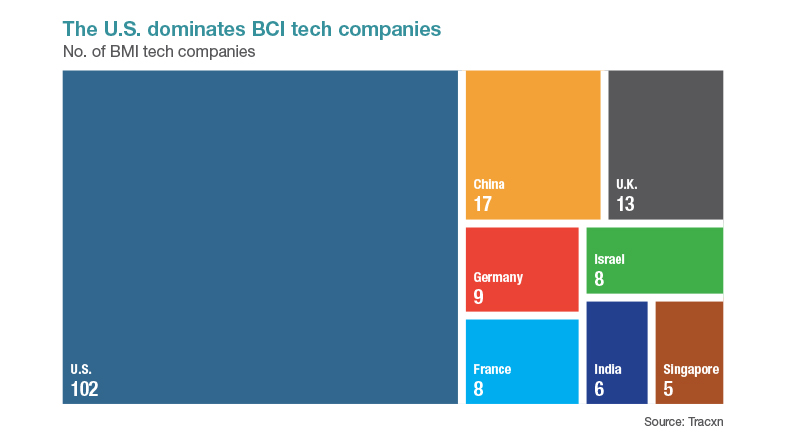
While the need for BCI technology is global, the research and development landscape is heavily concentrated in the U.S. and China. Most of the prominent companies in the field are also in th U.S. Widespread adoption will depend on several factors, including a robust regulatory framework addressing issues like data privacy, device safety, and ethical considerations. Public acceptance, likely to be higher for non-invasive technologies, will also play a crucial role.
Have a
story idea?
Tell us.
Do you have a recent research paper or an idea for a science/technology-themed article that you'd like to tell us about?
GET IN TOUCH